



Overview
-
 Western Blot analysis of various cells using PDHA1 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:2000
Western Blot analysis of various cells using PDHA1 Polyclonal Antibody diluted at 1:2000 -
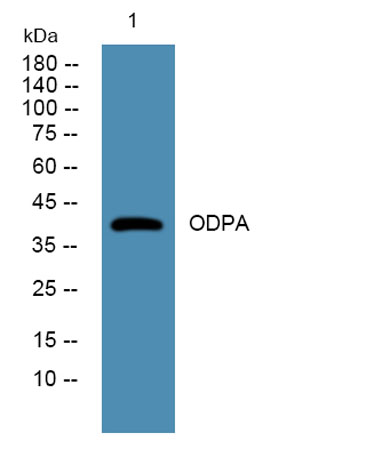 Western blot analysis of lysates from U2OS cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night
Western blot analysis of lysates from U2OS cells, primary antibody was diluted at 1:1000, 4°over night -
 Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 30min).
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 30min).
关闭
在线咨询
Online consultation
-
在线咨询
-
技术支持

关注微信公众号



 下载说明 ①
下载说明 ①




